Epiglottitis ┆Pediatric
Epiglottitis :.
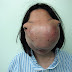
is an inflamation of the important part of the larynx - epiglottis, through the supraglottic region, including the arytenoid soft tissue, aryepiglottic folds, and sometimes the uvula.
is an inflamation of the important part of the larynx - epiglottis, through the supraglottic region, including the arytenoid soft tissue, aryepiglottic folds, and sometimes the uvula.
Causes
The epiglottis is content of flexible tissue (called cartilage) at the back of the tongue. It closes your windpipe (trachea) after you swallow therefore food doesn't enter your airways. This helps stop coughing or choking when swallowing.
Swelling of the epiglottis is Commonly caused by the bacteria Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae). it should also be caused by alternative bacteria or viruses associated withupper respiratory infections.
Epiglottitis is currently very uncommon, because the H. influenzae sort B (Hib) vaccine could be a routine childhood immunization. The disease was once {most most frequently seen in kids ages (two - six) . Rarely,epiglottitis can happen in adults.
The epiglottis is content of flexible tissue (called cartilage) at the back of the tongue. It closes your windpipe (trachea) after you swallow therefore food doesn't enter your airways. This helps stop coughing or choking when swallowing.
Swelling of the epiglottis is Commonly caused by the bacteria Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae). it should also be caused by alternative bacteria or viruses associated withupper respiratory infections.
Epiglottitis is currently very uncommon, because the H. influenzae sort B (Hib) vaccine could be a routine childhood immunization. The disease was once {most most frequently seen in kids ages (two - six) . Rarely,epiglottitis can happen in adults.
Symptoms
Epiglottitis Start with a high fever and sore throat. Other symptoms May contain:- Abnormal respiratory sounds (stridor)
- Chills, shaking
- Cyanosis (blue skin coloring)
- Drooling
- Dyspnea (patient may need to sit upright and lean slightly forward to breathe)
- Dysphagia
- Voice changes (hoarseness)
Exams and Tests
Epiglottitis is a medical emergency. You can get immediate medical assistance. use the tongue depressor in an attempt to examine the throat at home, as this can make the situation worse.The health care server performance may examine the larynx using either a small mirror or laryngoscope. This can be done this exam in the operating room in case of blocked trachea.
Tests that can be the following:
- Blood culture or throat culture
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Neck x-ray
Treatment
There is a need to stay in the hospital, usually in an intensive care unit (ICU).
Treatment includes methods to help the person to breathe, including:
- Breathing tube (intubation)
- Wet (humidified) oxygen
- Antibiotics to treat the infection
- Anti-inflammatory medicines (corticosteroids) to reduce throat swelling
- Fluids given intravenously (by IV)
Prognosis
Can be inflammation of the epiglottis in cases life-threatening emergency. However, with proper treatment, the result is usually good.Prevention
Immunization with the vaccine protects most children from epiglottitis.The bacteria that causes epiglottitis is contagious. If a person in your family is sick from this bacteria, you need to be tested and take adequate treatment .
Category: Pediatric












0 التعليقات